Build GenAI-Integrated Serverless Contact Forms for Static Websites With AWS Lambda, API Gateway, Bedrock, and SES
Build a serverless backend with generative AI capabilities for handling contact forms on static websites. This documentation covers the complete end-to-end solution, covering backend development with AWS services like API Gateway, Lambda, Bedrock, and Simple Email Service, as well as frontend integration with the contact form of a static website.
Submit a message using the Contact Form at digitalden.cloud to see the solution in action.
1. Introduction
Static websites have gained popularity due to their speed, security, and cost-effectiveness. They can be hosted on various platforms like:
- AWS
- GitHub Pages
- Netlify
However, static websites have a significant limitation: they lack the ability to handle dynamic operations, such as processing contact form submissions. Traditionally, adding this functionality required setting up and maintaining a server-based solution, which introduces several challenges.
The Challenge and Solution
A traditional server setup for contact form processing requires 24/7 server provisioning and management. While an Amazon EC2 instance could be used, it comes with several responsibilities:
- Continuous server operation, regardless of activity levels.
- Ongoing server maintenance, including regular updates and patches.
- Complex setup involving auto-scaling groups and load balancers to manage traffic fluctuations.
- Constant costs for maintaining minimum infrastructure, even during low usage periods.
These factors introduce additional complexity, expenses, and management overhead, potentially undermining the simplicity and cost-effectiveness that make static sites attractive.
To overcome this challenge and maintain the advantages of static site architecture, a serverless solution can be implemented to handle contact form submissions. This serverless approach comes with some great advantages:
- It only charges for the compute time used to process form submissions.
- The system automatically scales to handle varying loads without intervention.
- There’s no need to manage server infrastructure or worry about updates and patches.
- The solution can be easily integrated with any static website, regardless of its hosting platform.
With this serverless solution, dynamic functionality can be added to a static site without needing traditional server management, preserving the simplicity and cost-effectiveness that make static sites attractive.
Integrating Generative AI
You might be wondering why we’re integrating generative AI into the contact form solution. Let’s explore this:
- Many websites offer generic, pre-written responses to form submissions, which can feel impersonal. Incorporating generative AI into the contact form creates a unique experience for each user, potentially leaving them with a lasting impression.
- Integrating generative AI with serverless architecture demonstrates a practical application of emerging technologies in a common web feature, illustrating how advanced solutions can enhance routine online interactions such as submitting contact forms.
Objectives
By the end of this documentation, you will be able to:
- Create a serverless backend for handling contact form submissions
- Integrate Generative AI features into a serverless backend
- Implement automated email functionality
- Integrate a serverless backend with a contact form of a static website
Prerequisites
Before starting, ensure you have the following:
- AWS account with appropriate permissions to create and manage the required services.
- Registered domain to set up Amazon Simple Email Service (SES).
- Visual Studio Code with the Live Server extension installed (for local testing of your static website).
- HTML5 UP Dimensions Template to provide the static website’s contact form layout and design.
- Amazon Route 53 is recommended for easier DNS configuration.
- While you can use any domain registrar, domains not managed by Route 53 will require additional steps for SES verification.
Solution Architecture
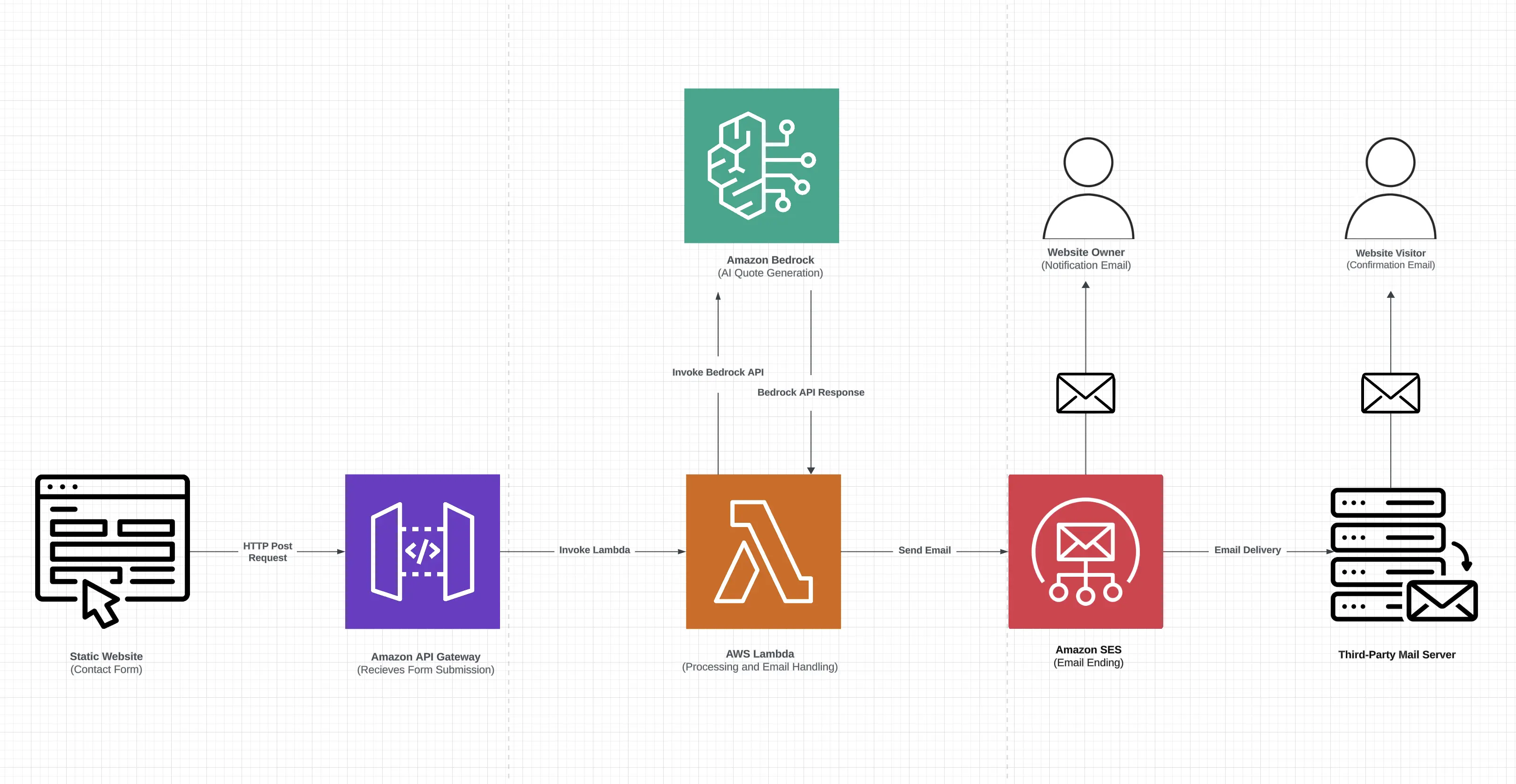
This solution architecture outlines a process for dynamically generating and delivering inspirational quotes using a combination of AWS services, including Amazon API Gateway, AWS Lambda, Amazon Bedrock, and Amazon Simple Email Service (SES).
Backend Integration
Contact Form Submission: The process begins with a static contact form hosted on your website. When a visitor submits this form, it triggers an HTTP POST request to Amazon API Gateway.
Request Handling by API Gateway: Amazon API Gateway receives the incoming request and invokes an AWS Lambda function designed to handle the form submission.
- Lambda Function Execution: The AWS Lambda function is the core component of this solution and is responsible for the following tasks:
- Processing the data submitted through the contact form.
- Utilizing a predefined prompt to request an inspirational quote generation.
- Invoking the Amazon Bedrock API to generate the quote based on the prompt.
Quote Generation with Amazon Bedrock: Amazon Bedrock processes the prompt provided by the Lambda function and generates a unique inspirational quote.
- Response Handling by Lambda Function: Upon receiving the response from Amazon Bedrock, the AWS Lambda function:
- Parses and formats the generated quote.
- Initiates an email-sending process using Amazon Simple Email Service (SES).
- Email Delivery with Amazon SES: Amazon SES manages the email delivery process by:
- Sending a notification email to the website owner, confirming the form submission and the generated quote.
- Sending a confirmation email, including the generated inspirational quote, to a third-party email service provider, which then delivers the email to the website visitor.
This backend architecture leverages AWS’s scalable and reliable services to seamlessly integrate form submission, dynamic content generation, and email delivery, providing an efficient and automated workflow for engaging with website visitors.
Frontend Integration
To integrate the static website frontend with the serverless backend, you will use the HTML5 UP Dimensions Template, which offers a modern design and is straightforward to set up and customize.
The following modifications will be made to the template’s contact form to facilitate communication with the backend services:
Update Form Action: Modify the form’s action attribute to point to the Amazon API Gateway endpoint URL.
Add Custom JavaScript:
- Capture form data when a user submits the contact form.
- Send the captured data as an HTTP POST request to the API Gateway.
- Implement HTML5 validation to ensure all required fields are filled correctly, including checks for valid email format and message length.
- Manage the user experience by displaying appropriate success or error messages based on the API response.
To test the modified frontend, you will use the Live Server extension in Visual Studio Code, which allows local testing and interaction with the backend API in a simulated production environment.
Roadmap
This documentation is structured as a progressive build-up, with each section dedicated to an AWS service required to create the solution:
graph TD
A[Introduction] --> B[Amazon SES]
B --> C[AWS Lambda]
C --> D[Amazon Bedrock]
D --> E[API Gateway]
E --> F[Frontend Integration]
Each section builds on the previous one, guiding you through the setup and configuration needed to create a fully functional, serverless contact form solution.
Lets build it!
2. Amazon Simple Email Service (SES)
flowchart LR
SES[Amazon SES] -->|Confirmation Email| Visitor[Visitor]
SES -->|Notification Email| Owner[Website Owner]
This section describes how to set up Amazon Simple Email Service (SES) to handle email communications for the serverless contact form solution.
Configuring Amazon SES enables the serverless backend to:
- Automatically send emails to visitors who fill out the contact form.
- Notify the website owner about new form submissions.
If you want to start building right away, you can skip to the Hands-On With SES section below. Otherwise, continue reading to learn more about the benefits, context, and configuration details of using Amazon SES with your serverless architecture.
What Is Amazon SES?
Amazon SES is a scalable, cloud-based email platform that simplifies email communications for businesses and developers. It offers a cost-effective solution for sending and receiving emails using custom email addresses and domains without the need to manage personal email servers.
Amazon SES supports various types of emails, including marketing, transactional, and informational messages. Beyond sending emails, it can receive and process incoming emails, enabling developers to build complex, email-based applications.
In the context of the serverless contact form solution, Amazon SES serves two primary purposes:
Sending Confirmation Emails to Visitors
When a visitor submits the contact form, Amazon SES automatically sends a confirmation email to the visitor. For example, upon form submission, the visitor receives an email stating:
“Thank you for your message. We’ve received your message and will respond soon.”
Notifying Website Owners of New Submissions
Amazon SES sends automated emails to the website owner for each new form submission, including the submitter’s details and message content.
Benefits of Using SES With Serverless Architecture
Amazon SES offers several advantages when integrated with serverless architectures, especially for contact form implementations.
Traditional email systems can become complex and costly as a website scales. They often require:
- Email Server Management
- Network Configuration
- IP Reputation Management
While third-party email services provide alternatives, they may involve complex contracts, pricing structures, and significant upfront costs.
By leveraging Amazon SES, these challenges are mitigated:
- Email server management is fully handled by Amazon.
- Emails are sent through Amazon’s robust and reliable network infrastructure.
- Benefit from Amazon’s reputable IP addresses for improved email deliverability.
Scalability is a key advantage of Amazon SES. Whether the website receives ten form submissions per day or ten thousand, SES seamlessly scales to handle the load without additional configuration. This aligns with serverless architecture principles, allowing developers to focus on building features rather than managing infrastructure.
The Sandbox Mode
When first using Amazon SES, accounts are placed in sandbox mode as a default security measure. In sandbox mode, there are two key restrictions:
- Emails can be sent only from addresses or domains that have been verified in Amazon SES.
- Emails can be sent only to addresses or domains that have been verified.
These limitations impact the functionality of a serverless contact form, particularly when attempting to send confirmation emails to users who submit the form.
Email Verification Methods
To overcome sandbox restrictions, Amazon SES provides two methods for verifying the ability to send emails:
Verifying Individual Email Identities
- Process:
flowchart LR
A[Enter email address in SES console] --> B[SES sends verification email]
B --> C[Click verification link in email]
C --> D[Email address verified in SES]
- Limitations:
- Emails can only be sent to verified addresses in sandbox mode, making it impractical for public-facing contact forms, as visitors’ email addresses cannot be pre-verified.
- Requires separate verification for each sender address, which is inefficient as the number of addresses grows.
Verifying a Domain
- Process:
flowchart LR
A[Verify ownership of entire domain] --> B[Send emails from any address within that domain]
B --> C[contact@example.com]
B --> D[support@example.com]
- Advantages:
- More scalable for growing solutions.
- Presents a professional appearance with consistent domain-based email addresses.
- Considerations:
- Requires access to the domain’s DNS settings, involving a slightly more complex setup.
- Simplified if the domain is managed by Amazon Route 53, as AWS can automate DNS configuration.
Moving to Production
To enable full functionality of a public-facing contact form, it’s necessary to move beyond sandbox mode. This transition involves two steps:
flowchart LR
A[Verify Domain Ownership] --> B[Submit Production Access Request]
B --> C[Account Moved Out of Sandbox Mode]
Once in production, the following capabilities become available:
- Confirmation emails can be sent to any email address without prior verification.
- Utilize any email address within the verified domain without individual verifications.
- The contact form functions fully in a production environment.
Hands-On With SES
To configure Amazon SES for your serverless contact form solution, you will perform the following tasks:
- Create and verify an individual email identity
- Set up domain verification
- Move out of the sandbox into production
Task 1: Create and Verify an Individual Email Identity
Select Your AWS Region
Amazon SES is a regional service, so start by logging into the AWS Management Console and selecting the AWS Region where you plan to use SES.Access the Amazon SES Console
Go to the Amazon SES console to begin setting up your email identity.Create an Email Identity
In the SES console, under Email Addresses, click Create Identity. Choose Email Address as the identity type, enter the email address you want to verify, and click Create Identity.Verify the Email Address
AWS will send a verification email to the specified address. Check your inbox, and click the verification link to confirm ownership of the email address.Confirmation
Once verified, a confirmation message will appear in the SES console. At this point, your account is still in sandbox mode, meaning certain sending restrictions apply.
Task 2: Set Up Domain Verification
Initiate Domain Verification
In the SES console, click Create Identity, select Domain as the identity type, and enter your domain name.Configure DKIM Settings
Enable Easy DKIM to have Amazon SES sign outgoing emails with DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM). This step is important for authenticating your emails and improving deliverability.Assign Configuration Set (Optional)
If you’re not using configuration sets, leave the Assign a Default Configuration Set checkbox unchecked. Configuration sets allow you to apply specific rules to your email sending and can be configured later as your needs grow.Set Up a Custom MAIL FROM Domain
Enable Customize MAIL FROM Domain to use a custom subdomain, like mail.example.com or ses.example.com for your email’s “MAIL FROM” address. This step separates your email sending from your primary domain, helping to manage your domain’s reputation.- DNS Configuration
- Using Amazon Route 53: AWS can automatically add the necessary DNS records for DKIM and MAIL FROM configurations.
- Using a Third-Party DNS Provider: Manually add the DNS records provided by Amazon SES (CNAME for DKIM, MX, and TXT for MAIL FROM) to your DNS settings.
- Complete Domain Verification
Click Create Identity to start the verification process. This may take a few minutes. Monitor the Identities page for the status of your domain verification and DKIM setup. AWS will send confirmation emails once the domain is successfully verified.
Task 3: Move Out of the Sandbox into Production
To use Amazon SES in a live environment and send emails to unverified recipients, you need to move out of the sandbox mode.
Review Sending Limits
In the SES console, go to Account Dashboard to review your current sending limits and sandbox status.Request Production Access
Click Request Production Access to initiate the process. You’ll need to fill out the Email Sending Limits form, providing key information such as:- Mail Type: Choose Transactional for emails triggered by specific actions, like form submissions.
- Website URL: Enter the URL where your contact form is hosted.
Use Case Description: Clearly describe your use case. For example:
“I am building a serverless contact form handler as part of an AWS Solution for my static website. This project integrates various AWS services, including Simple Email Service, Lambda, API Gateway, and Bedrock. The form handler will send confirmation emails to form submitters and notifications to me as the website owner. The expected email volume is low, approximately 5-10 emails per week. This solution helps me apply my AWS knowledge and understand cloud architecture in a practical setting, while also providing a functional contact method for my site visitors.”
Submit Your Request
AWS typically processes these requests within one business day. Once approved, your account will move out of sandbox mode, allowing you to send emails to unverified recipients.
3. AWS Lambda
flowchart LR
Lambda[AWS Lambda] -->|Generate AI Quote| Bedrock[Amazon Bedrock]
Lambda -->|Send Notification Email| SES[Amazon SES]
Lambda -->|Send Confirmation Email| SES
SES -->|Email to Visitor| Visitor[Visitor]
SES -->|Email to Website Owner| Owner[Website Owner]
This section describes how to configure AWS Lambda to handle the core processing logic for your serverless contact form solution.
Configuring AWS Lambda allows you to:
- Automatically process form submissions received through API Gateway.
- Integrate with Amazon Bedrock to generate AI content.
- Send confirmation and notification emails using Amazon SES.
If you want to start building right away, you can skip to the Hands-On With Lambda section below. Otherwise, continue reading to learn more about the benefits, context, and configuration details of using AWS Lambda within your serverless architecture.
What Is AWS Lambda
AWS Lambda is a serverless compute service that allows you to run code without the need to provision or manage servers. It provides cloud-based processing power to run applications and execute code, acting as a virtual server to perform calculations and process data.
For this serverless contact form, Lambda eliminates the need to manage underlying infrastructure, enabling you to focus solely on developing the logic to handle form submissions. AWS automatically manages the compute resources required to run your code, making the process efficient and straightforward.
Key Features and Role of AWS Lambda in the Contact Form Solution
AWS Lambda offers several key features that make it ideal for building scalable, efficient, and cost-effective serverless applications. Here’s how these features specifically benefit the contact form solution:
Event-Driven Architecture
AWS Lambda utilizes an event-driven model, where specific events or triggers activate functions. These events can include HTTP requests, file uploads to S3, or custom application events.
Upon detection of an event, Lambda automatically executes the corresponding code, processes the data, and manages the required compute resources. Once the code execution completes, Lambda remains idle, ready for the next event.
The contact form handler function will leverage Lambda’s event-driven architecture as follows:
Form Submission as an Event: The process begins when a visitor submits the contact form. JavaScript embedded in the static website captures this submission and sends an HTTP POST request to Amazon API Gateway, which serves as the event trigger.
Function Activation: Upon detecting this event, Lambda activates the function and executes the code based on the configured settings, such as memory allocation and execution time.
- Event Data Processing: The function processes the form submission data by:
- Sending a notification email to the website owner.
- Generating an inspirational quote using Amazon Bedrock.
- Sending a confirmation email to the submitter with the AI-generated quote.
Completion and Resource Release: Once all tasks are complete, Lambda terminates the function, releasing the allocated resources.
- Waiting for the Next Event: Lambda remains in a waiting state, ready to process the next submission.
This event-driven model provides a scalable, efficient solution for handling contact form submissions without requiring a constantly running server.
Automatic Scaling
AWS Lambda features automatic scaling, adjusting its processing capacity based on the volume of incoming requests. This means that Lambda dynamically scales the resources allocated to your function according to demand.
Automatic scaling provides several advantages for the contact form handler:
- Handling Concurrent Submissions: Lambda processes multiple submissions simultaneously, without creating queues.
- Adapting to Varying Workloads: Whether handling a single submission per day or hundreds suddenly, Lambda adjusts its capacity instantly.
- Efficient Task Management: Lambda can process new submissions while completing time-consuming tasks, like generating quotes or sending emails, ensuring minimal wait times.
Concurrent Execution and Rapid Scaling
Lambda supports concurrent execution, allowing it to handle multiple function invocations at the same time, akin to having multiple workers processing tasks in parallel. For our contact form, this ensures simultaneous processing of multiple submissions.
Lambda scales rapidly, adding capacity to handle 1,000 more submissions every 10 seconds, scaling up automatically until reaching the AWS account’s concurrency limit. These capabilities are built into the standard Lambda service without extra costs or configurations.
Cost-Effectiveness With Pay-Per-Use Pricing
AWS Lambda uses a pay-per-use pricing model, ideal for serverless applications or those with unpredictable usage patterns. Here’s how it works:
- Flexible Cost Structure: You are only charged for the compute time your function uses.
- Granular Pricing: Charges are based on the number of requests and the execution time, measured in milliseconds.
For example, traditional servers incur costs around the clock, regardless of usage. With Lambda, costs are incurred only when the function processes requests, eliminating the need for capacity planning and server management.
Lambda’s pricing model provides the following benefits:
- Charges apply only when processing submissions, common for most websites.
- During periods of low activity, costs are minimal.
- Lambda handles sudden spikes in form submissions without additional configurations or costs.
- No need for a constantly running server, reducing overall expenses.
Integration With Other AWS Services
Lambda integrates seamlessly with various AWS services, enabling the development of sophisticated solutions without unnecessary complexity. For the contact form handler, Lambda interacts with:
- API Gateway - Manages HTTP requests from the contact form.
- Simple Email Service (SES) - Manages email confirmations and notifications.
- Amazon Bedrock - Generates AI-driven inspirational quotes.
Streamlined Development
Lambda removes the complexity of server management, allowing you to focus on writing code. For this solution, it means concentrating on processing submissions and leveraging integrated services.
Without Lambda, a traditional server-based approach would involve:
- Server setup and configuration.
- Web server management.
- Application environment setup.
- Complex scaling configurations.
- Ongoing monitoring and maintenance.
With Lambda, these infrastructure tasks are unnecessary, letting you focus solely on functionality.
Considerations
While Lambda offers numerous benefits, it is essential to consider the following:
Cold Starts: Functions may experience slight delays on the first invocation after a period of inactivity, which could impact some applications. For the contact form solution, cold starts are unlikely to significantly affect user experience due to the sporadic nature of form submissions.
Stateless Execution: Lambda functions do not retain state between executions. For scenarios where state persistence is required, such as tracking the number of forms submitted by an individual, additional AWS services like DynamoDB or SQS should be used. In our contact form solution, stateless execution is appropriate, as each submission is handled independently.
Resource Limits: Lambda functions have certain constraints, including up to 10GB of memory and a maximum execution time of 15 minutes. These resource limits are more than sufficient for processing form submissions, generating AI-driven quotes, and sending emails in our serverless contact form handler.
Now that we’ve covered the critical aspects of implementing Lambda for this solution, let’s proceed with building the serverless contact form handler in the AWS Management Console.
Hands-On With Lambda
To configure AWS Lambda for your serverless contact form solution, you will follow these tasks:
- Create and configure a Lambda function
- Set up function settings
- Configure permissions and roles
- Implement the function code
- Set up environment variables
- Test the Lambda function
Task 1: Create and Configure a Lambda Function
Access the AWS Console
Go to the AWS Lambda service.Create a New Lambda Function
Click Create function and select Author from scratch. Name your function ContactFormHandler and choose the latest Python runtime version.Configure Permissions
An execution role is an IAM role that grants the Lambda function permission to access AWS services and resources.- Keep the default option to allow the function to upload logs to CloudWatch. You’ll add specific permissions for Amazon Bedrock and Amazon SES later to enable the function to utilize these services effectively.
Task 2: Set Up Function Settings
Configure General Settings
Once the function is created, go to the Configuration tab and adjust the following settings:Memory Allocation
Keep the default memory allocation of 128 MB, which is sufficient for processing form submissions and making API calls.Set the Timeout
Set the timeout to 10 seconds to ensure the function has enough time to process submissions, generate quotes, and send emails.
After deploying the function, use CloudWatch Logs to monitor its performance. The logs will display memory usage and execution duration, helping you fine-tune these settings based on actual performance data.
Task 3: Configure Permissions and Roles
To enable your Lambda function to interact with other AWS services, you need to configure its execution role’s permissions. This ensures that the function has the necessary access rights to perform tasks such as sending emails with Amazon SES and generating AI content with Amazon Bedrock.
Configuring Lambda Function Permissions
Access the Permissions Section
In the Lambda console, go to the left sidebar and click on Permissions to view and modify the function’s permissions.Review the Existing Execution Role
An execution role was automatically created when the function was set up. This role currently includes CloudWatch Logs permissions, allowing the function to create log groups, create log streams, and write log events.Add Specific Permissions for Amazon SES and Amazon Bedrock
Click on the role name to open the IAM console in a new tab. To grant additional permissions for Amazon SES and Amazon Bedrock, you will create custom inline policies for these services.
Create a Policy for Amazon SES
- Create an Inline Policy for Amazon SES
- Under Add permission, select Create inline policy from the dropdown menu. This will create a custom policy specifically for the Lambda function, which is useful for unique, one-off situations.
- In the Service field, search for and select SES.
- Under Actions allowed, select Write and check SendEmail. This grants the function permission to send email messages, which is essential for its operation.
- Restrict Access by Resources
- Under Resources, select Specific and click Add ARNs.
- Under Identity, click Add ARNs to restrict access to specific email addresses or domains. This precisely controls which email addresses or domains the function can use as senders.
- Specify Email Addresses or Domains: Indicate the specific email addresses or domains from which the function is allowed to send emails. This secures the function and prevents potential misuse.
- Define Resource Scope
- For Resource in, keep the default ‘This account’ to ensure that the function operates within your AWS account, preventing any cross-account access.
- For Resource region, enter the region where the SES account is set up. This specifies which regional SES service the function will use.
- For Resource identity name, enter the domain name that is verified in SES. This further restricts the function’s capabilities to only send emails from the specified domain.
- Finalize the SES Policy
- Click Add ARNs to add the specified domain to the policy.
- Click Next, enter a policy name (SES-SendEmail-Policy), and click Create policy.
The policy created allows the Lambda function to send emails only from the specified domain and region, providing flexibility to use any email address within the domain without modifying the policy for each new address. This approach also applies the principle of least privilege, limiting permissions to a specific domain and region to reduce potential security risks while maintaining flexibility.
Create a Policy for Amazon Bedrock
- Create an Inline Policy for Amazon Bedrock
- Click Create inline policy again, and select Bedrock from the Service dropdown.
- Under Actions allowed, select Read and check InvokeModel. This grants the function permission to use Bedrock’s models to generate text.
- Define Resource Scope for Bedrock
- Under Resources, choose All resources to allow the Lambda function to invoke any Bedrock model without restriction. While this is less restrictive, it provides flexibility to experiment with different models without needing to change the policy frequently.
- Finalize the Bedrock Policy
- Click Next, name the policy (Bedrock-InvokeModel-Policy), and click Create policy.
- Attach the Bedrock Policy to the Execution Role
Return to the Lambda console and refresh the Execution Role. In the Resource summary, you should now see Amazon Bedrock, Amazon SES, and CloudWatch Logs listed. This confirms that the function has the necessary permissions to interact with all required services.
Task 4: Implement The Function Code
To build the core logic for your serverless contact form handler, you need to implement the function code for AWS Lambda. This involves creating and deploying Python scripts that handle incoming form submissions, generate AI content, and send emails through Amazon SES. These scripts will enable your Lambda function to process user inputs efficiently, invoke Amazon Bedrock for inspirational quotes, and communicate with users and website owners via email.
- Prepare the Python Scripts
The Lambda function requires two Python files: one for the main function logiclambda_function.pyand another for the quote generation templatetemplate.py. Below are the scripts you need to implement:
lambda_function.py:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165
import json import boto3 import os import logging from botocore.exceptions import ClientError from template import generate_inspirational_quote_template # Set up logging logger = logging.getLogger() logger.setLevel(logging.INFO) # Configuration from environment variables RECEIVER = os.environ['RECEIVER_EMAIL'] SENDER = os.environ['SENDER_EMAIL'] SENDER_NAME = os.environ['SENDER_NAME'] SES_REGION = os.environ['SES_REGION'] BEDROCK_REGION = os.environ['BEDROCK_REGION'] MODEL_ID = os.environ['BEDROCK_MODEL_ID'] # Validate required environment variables required_vars = [RECEIVER, SENDER, SENDER_NAME, SES_REGION, BEDROCK_REGION, MODEL_ID] if not all(required_vars): raise EnvironmentError("Missing one or more required environment variables") # Initialize AWS service clients ses = boto3.client('ses', region_name=SES_REGION) bedrock = boto3.client('bedrock-runtime', region_name=BEDROCK_REGION) def lambda_handler(event, context): """ Main handler function for the Lambda. Processes incoming events, sends emails, and generates quotes. """ try: # Parse the incoming event data data = json.loads(event.get('body', '{}')) logger.info(f"Received message from {data.get('name', 'unknown')}") # Log environment variables for debugging logger.info(f"Environment Variables - RECEIVER: {RECEIVER}, SENDER: {SENDER}, SENDER_NAME: {SENDER_NAME}, MODEL_ID: {MODEL_ID}") # Send notification email about the new form submission send_notification_email(data) try: # Generate an inspirational quote quote = generate_inspirational_quote() except Exception as e: logger.error(f"Error generating inspirational quote: {str(e)}") quote = "'Believe in yourself and all that you are.'" # Fallback quote if generation fails # Send response email to the user with the generated quote send_user_response_email(data, quote) # Return success response return response(200, {'result': 'Success'}) except Exception as e: # Log any unexpected errors logger.error(f"Error: {str(e)}", exc_info=True) # Return error response return response(500, {'result': 'Failed', 'error': str(e)}) def send_notification_email(data): """ Sends a notification email about a new form submission. """ try: # Construct the email body email_body = ( f"New contact form submission:\n\n" f"Name: {data['name']}\n" f"Email: {data['email']}\n" f"Message: {data['message']}" ) # Send the email using Amazon SES response = ses.send_email( Source=f"{SENDER_NAME} <{SENDER}>", Destination={'ToAddresses': [RECEIVER]}, Message={ 'Subject': {'Data': f"[Contact Form] New submission from {data['name']}"}, 'Body': {'Text': {'Data': email_body}}, }, ReplyToAddresses=[data['email']] ) logger.info(f"Notification email sent to {RECEIVER}. Message ID: {response['MessageId']}") except ClientError as e: logger.error(f"Error sending notification email: {e.response['Error']['Message']}") def generate_inspirational_quote(): """ Generates an inspirational quote using the Bedrock AI model. """ # Get the quote template prompt = generate_inspirational_quote_template() # Prepare the request for the AI model native_request = { "prompt": f"Human: {prompt}\nAssistant:", "max_tokens_to_sample": 150, "temperature": 0.9, "top_p": 0.9, } # Call the Bedrock AI model response = bedrock.invoke_model( modelId=MODEL_ID, body=json.dumps(native_request), contentType='application/json', accept='application/json' ) model_response = json.loads(response['body'].read()) quote = model_response['completion'].strip() # Clean up the quote and wrap it in single quotes quote = quote.strip('"').strip("'").strip() quote = "'" + quote + "'" return quote def send_user_response_email(data, quote): """ Sends a response email to the user with the generated inspirational quote. """ # Construct the email body email_body = ( f"Hi {data['name']},\n\n" f"Thanks for reaching out through my website. I've received your message and will get back to you soon.\n\n" f"In the meantime, here's an inspirational quote to brighten your day:\n\n" f"{quote}\n\n" f"Kind regards,\n" f"{SENDER_NAME}\n\n" f"{data['name']}, this quote was uniquely generated by AI (Amazon Bedrock) just for you." ) logger.info(f"Email body: {email_body}") try: # Send the email using Amazon SES response = ses.send_email( Source=f"{SENDER_NAME} <{SENDER}>", Destination={'ToAddresses': [data['email']]}, Message={ 'Subject': {'Data': f"Thank you for contacting {SENDER_NAME}"}, 'Body': {'Text': {'Data': email_body}}, } ) logger.info(f"User response email sent to {data['email']}. Message ID: {response['MessageId']}") logger.info(f"SES send_email response: {response}") except ClientError as e: logger.error(f"Error sending user response email: {e.response['Error']['Message']}") def response(status_code, body): """ Generates a standardized response object for the API Gateway. """ return { 'statusCode': status_code, 'body': json.dumps(body), 'headers': { 'Content-Type': 'application/json', 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*', }, } # Log that the Lambda function is configured and ready logger.info("Lambda function configured and ready.")
template.py:1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38
def generate_inspirational_quote_template(): """ Generates a template for requesting an inspirational quote from an AI model. Returns: str: A formatted string containing the prompt template for generating an inspirational quote. """ # Define the template string template = """ Generate a unique, original, and thought-provoking inspirational quote about life, success, or personal growth. Important: 1. Provide ONLY the quote text. 2. Do not include any introductory phrases or explanations. 3. The quote should be inspirational and universally applicable. 4. Begin your response with the quote directly, without any preamble. Now, provide an original inspirational quote: """ return template # NOTES: # 1. This template is designed for use with AI language models. # 2. It provides clear instructions to generate a standalone quote. # 3. The output is easy to extract and use without additional processing. # CUSTOMIZATION: # - To change the theme: # Replace "life, success, or personal growth" with your desired topic. # Example: "technology, nature, or creativity" # - To adjust the style: # Add style instructions in the "Important" section. # Example: "5. The quote should have a motivational tone." # - To specify an audience: # Add audience information in the "Important" section. # Example: "5. The quote should be suitable for a young adult audience."
- Deploy the Code
- Copy the content from the
lambda_function.pyfile and paste it into the Lambda console’s code editor. - In the Lambda console, create a new file named
template.pyand paste the template code provided above.
- Copy the content from the
- Deploy the Changes
Click Deploy to save and apply the changes to the Lambda function.
Task 5: Set Up Environment Variables
To ensure your Lambda function operates correctly, you must configure environment variables that provide essential configuration settings for the function. These variables allow the function to dynamically access necessary information like email addresses and AWS region settings without hardcoding values in the code. This approach improves flexibility, security, and maintainability.
Define Environment Variables
Access Environment Variables in the Lambda Console
Go to the Configuration tab in the Lambda console and select Environment variables. Click Edit to add the necessary environment variables.Add the Required Environment Variables
Enter the following key-value pairs:RECEIVER_EMAIL: The email address where notifications about form submissions will be received.
Example:your-email@example.comSENDER_EMAIL: The address that will appear as the sender of the emails. Since the entire domain is verified in Amazon SES, any email address within the domain can be used without verifying individual addresses. Example:
noreply@example.com,contact@example.com, or any other preferred prefix.SENDER_NAME: The name that will appear alongside the sender’s email address. This could be a name, company, or website name.
Example:DigitalDenCloudSES_REGION: The AWS region where Amazon SES is configured. This should match the region where your SES domain is verified.
Example:eu-west-2BEDROCK_REGION: The AWS region where Amazon Bedrock is available. This should be a region where Bedrock services can be accessed.
Example:eu-west-2BEDROCK_MODEL_ID: The ID of the Bedrock AI model to use for generating inspirational quotes.
Example:anthropic.claude-v2:1
Save the Environment Variables
After entering all the environment variables, click Save to apply the changes.
Task 6: Test The Lambda Function
To ensure that your Lambda function operates correctly, test it with a simulated form submission. This testing will help verify that the function processes data as expected, generates quotes, sends emails, and handles errors effectively. By testing early, you can identify and resolve issues before integrating with other AWS services like API Gateway.
Create and Configure a Test Event
Create a Test Event
Go to the Code tab in the Lambda console, click Test, and then select Configure test event. Give the test event a name, such as TestFormSubmission.Configure the Test Event JSON
Copy the following test event JSON and paste it into the test event editor, replacing any existing code:1 2 3
{ "body": "{\"name\":\"John Doe\",\"email\":\"your-email@example.com\",\"message\":\"This is a test message.\"}" }
Replace your-email@example.com with your actual email address. This email is where you will receive the test email messages.
Run the Test
Save the test event, click Test to run the function, and expand the details to review the results. This test will help you:- Verify form data processing.
- Check quote generation.
- Test email sending.
- Confirm error handling and logging.
Test Results Summary
Expected Results
The Lambda function should successfully process the simulated form submission, demonstrating that the basic structure of the contact form handler is operational. However, you will encounter a specific issue during the test.Observed Behavior
The function sends two emails as intended: a notification to the specified receiver and a confirmation to the form submitter. The confirmation email includes a fallback quote rather than an AI-generated one. This fallback quote, integrated into the script, is triggered due to an error in the AI quote generation process with Bedrock. This error highlights a critical issue that must be addressed to implement the intended AI functionality.Verify Email Results
Check the received emails for notifications and confirmation messages. Confirm that the emails are sent from the SENDER_EMAIL address with the SENDER_NAME as specified in the environment variables.Investigate Bedrock Issue Using CloudWatch Logs
To further investigate the Bedrock issue, go to the Monitor tab on the Lambda function page and click View CloudWatch logs. This will open the CloudWatch Logs console, where you can analyze log streams.- Log Streams Overview: Each log stream represents a separate instance of the Lambda function’s execution. These streams contain logs generated during each function invocation, allowing you to track and debug individual executions.
- Locate Error Messages: Look for the error message related to the Bedrock model invocation, explaining why the AI quote generation failed. The error occurred due to a lack of access to the specified Bedrock model.
Despite the issue with Bedrock access, the Lambda function demonstrated resilience through its fallback mechanism. It successfully processed the form submission and sent the required emails, albeit with a pre-written quote.
To implement the intended AI functionality, you will address the Bedrock model access issue by requesting appropriate permissions.
4. Amazon Bedrock
flowchart LR
Lambda[AWS Lambda] -->|Invoke Bedrock API| Bedrock[Amazon Bedrock]
Bedrock -->|Use Model| Claude[Claude Anthropic]
Claude -->|Generate Inspirational Quotes| Bedrock
Bedrock -->|Return Quote| Lambda
This section describes how to use Amazon Bedrock to enhance your serverless contact form solution with generative AI capabilities.
Configuring Amazon Bedrock allows you to:
- Leverage high-performance foundation models for various AI tasks.
- Use a single, unified API to integrate AI models from different providers.
- Generate dynamic content, such as inspirational quotes, within your serverless solution.
If you want to start building right away, you can skip to the Hands-On With Bedrock section below. Otherwise, continue reading to learn more about Amazon Bedrock’s core concepts, capabilities, and its role in your serverless solution.
What is Amazon Bedrock?
Amazon Bedrock is a fully managed service that provides access to foundation models (FMs) from leading AI startups and Amazon through a single, unified API. This service enables you to integrate powerful AI capabilities into your applications without managing the complexities of different model providers.
Bedrock’s Role in The Serverless Contact Form
In your serverless contact form solution, Amazon Bedrock is used to generate personalized content for visitors who submit messages through the contact form. By integrating Bedrock’s foundation models, your Lambda function can create unique and engaging responses — like inspirational quotes — that enhance the user experience.
When a visitor submits a contact form, the Lambda function invokes Amazon Bedrock’s Anthropic Claude model to generate a dynamic, AI-driven quote. This quote is then sent back to the visitor in a confirmation email, adding a personalized touch to the interaction and making your website stand out.
Foundation Models
Foundation models are large-scale machine learning models trained on vast amounts of data. These models serve as a base for various specific tasks, such as natural language processing or image recognition. They are highly versatile and capable of handling numerous AI-driven applications, including:
- Generating human-like text
- Understanding and analyzing written content
- Translating between languages
- Answering questions based on given information
- Assisting with code writing and debugging
- Creating image descriptions or generating images from text prompts
Single, Unified API
While foundation models offer powerful capabilities, integrating them into applications can be complex, especially when dealing with multiple models from different providers. Amazon Bedrock simplifies this by providing a single, unified API that allows you to interact with all the foundation models through a consistent interface.
This unified approach makes it easier to integrate AI capabilities into your serverless contact form handler. By using one consistent method, you can quickly switch between different AI models to best suit your needs — whether generating multilingual quotes or creating more complex AI-driven responses.
Comparison: Amazon Bedrock vs. Other AI Services
To better understand Amazon Bedrock’s capabilities, let’s compare it to other AI services like OpenAI’s GPT:
- Model Variety: Bedrock offers models from multiple providers, while OpenAI GPT primarily offers its own models.
- Integration: Bedrock seamlessly integrates with other AWS services.
- Customization: Bedrock provides more options for fine-tuning and customizing models to specific needs.
- Data Privacy: Bedrock runs within your AWS environment, offering better data control.
- Specialized Tasks: Bedrock includes models optimized for specific tasks like text generation, summarization, and image generation.
In the serverless contact form handler, using the Anthropic Claude model anthropic.claude-v2:1 via Amazon Bedrock provides powerful natural language understanding capabilities for generating inspirational quotes.
Why Use Amazon Bedrock?
One of Bedrock’s key advantages is its model variety. For your solution, the Anthropic Claude model works well now, but in the future, you could easily switch to other models — like the Cohere Command model for multilingual quotes — by changing the BEDROCK_MODEL_ID environment variable in your Lambda function. This flexibility allows you to adapt and experiment with different AI models to meet evolving needs and preferences.
Amazon Bedrock’s Providers and Use Cases
Amazon Bedrock offers foundation models from various providers, each bringing unique strengths to the platform and opening up a wide array of possibilities for different use cases:
- Text Generation: The Anthropic Claude model excels at creating original content such as short stories, essays, and blog posts, with advanced language understanding and generation capabilities.
- Virtual Assistants: The AI21 Jurassic-2 model offers robust natural language understanding and generation, capable of understanding requests, breaking down tasks, and engaging in dialogue.
- Text and Image Search: The Cohere Command model provides strong semantic understanding and retrieval capabilities for searching through text and image data.
- Text Summarization: The Amazon Titan Text models are adept at creating concise summaries of long documents and extracting important information quickly.
- Image Generation: The Stability AI Stable Diffusion XL model can create realistic images based on text descriptions, useful for design and advertising.
Guardrails and Responsible AI
Amazon Bedrock also provides built-in responsible AI features, known as guardrails, which help implement safeguards tailored to your application requirements and responsible AI policies. These guardrails ensure ethical use and compliance with relevant standards.
Hands-On With Bedrock
To integrate Amazon Bedrock’s generative AI capabilities into your serverless contact form solution, follow these tasks:
- Set Up Model Access
- Test Bedrock Integration
To use Amazon Bedrock foundation models, you must ensure you have the appropriate access. An IAM user with sufficient permissions must request access to these models through the console. Once access is granted, it is available for all users in the account for the specified region.
Task 1: Set Up Model Access
Access the Bedrock Console
Go to the Model Access page in the Amazon Bedrock console to manage access to foundation models.Enable Model Access
Choose to enable specific models by selecting the checkbox next to the Anthropic Claude v2.1 model, which will be used to generate AI content like inspirational quotes.Save Changes
Click Save changes. This process may take a few minutes to complete.Verify Access Status
Once your request is approved, the access status will change to Access Granted. This grants all users in the account access to the specified models in the chosen region.
Task 2: Test Bedrock Integration
Now that you have enabled access to the Claude models, it’s time to test the integration with your Lambda function to ensure it generates AI quotes dynamically.
Initiate the Lambda Function Test
Return to your Lambda function and initiate the test event. The function should execute with the newly granted permissions, invoking Amazon Bedrock to generate an AI-generated quote.Verify the Output
After the test, check your email for a confirmation message. The email should now contain a unique AI-generated inspirational quote, replacing the static fallback text.
This test confirms that your Lambda function is correctly leveraging the Anthropic models via Amazon Bedrock to dynamically generate content, thereby enhancing the personalization and effectiveness of your serverless contact form solution.
5. Amazon API Gateway
flowchart LR
APIGateway[Amazon API Gateway] -->|POST Request| Lambda[AWS Lambda]
This section describes how to use Amazon API Gateway to create a RESTful API that will serve as the entry point for form submissions from your static website. The API Gateway connects the frontend to your AI-integrated serverless backend, completing the core infrastructure of your contact form system.
Configuring Amazon API Gateway allows you to:
- Handle form submissions from your static website efficiently.
- Integrate seamlessly with AWS Lambda for backend processing.
- Secure your API with authentication and authorization features.
- Monitor and optimize performance with detailed metrics and logging.
If you want to start building right away, you can skip to the Hands-On With API Gateway section below. Otherwise, continue reading to learn more about the benefits, context, and setup details of using Amazon API Gateway in your serverless architecture.
Understanding APIs
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of rules and protocols that enable different software applications to communicate with each other.
flowchart LR
Client["Client"] -->|Request| API["API (Waiter)"]
API -->|Forward to| Backend["Backend (Kitchen)"]
Backend -->|Response| API
API -->|Deliver Response| Client
Think of an API like a waiter in a restaurant:
- Request: You place an order with the waiter (API).
- Backend System: The waiter takes your order to the kitchen (backend system).
- Response: The waiter brings your food back to you (response).
In web development, APIs typically operate over HTTP, allowing clients (such as web browsers or mobile apps) to send requests to servers and receive responses.
Common HTTP methods in APIs include:
- GET: Retrieves data from the server (fetching a list of blog posts).
- POST: Sends data to the server to create a new resource (submitting a contact form).
- PUT: Updates an existing resource on the server (updating user profile information).
- DELETE: Removes a resource from the server (deleting a user account).
In your serverless contact form handler, you’ll use the POST method. When a user submits the form, their browser will send a POST request to your API, including all the contact form data in the request body.
What is Amazon API Gateway?
Amazon API Gateway is a fully managed service that allows you to create, publish, maintain, monitor, and secure APIs at any scale. In serverless architectures, API Gateway acts as the front door for applications accessing backend services, such as AWS Lambda.
For your solution, API Gateway will receive form submissions from your static website, route them to your Lambda function for processing, and return the responses back to the static website. The static website will then display the responses to the user.
flowchart LR
User["User"] -->|Interacts| StaticWebsite["Static Website"]
StaticWebsite -->|Form Submission| APIGateway["API Gateway"]
APIGateway -->|Invoke Lambda| LambdaFunction["Lambda Function"]
LambdaFunction -->|Process Data and Return Result| APIGateway
APIGateway -->|Return Response| StaticWebsite
StaticWebsite -->|Display Response| User
Benefits of Using API Gateway in Your Serverless Contact Form Solution
Scalability: API Gateway automatically scales to handle varying levels of traffic without the need for infrastructure management. If your contact form receives a surge in submissions, API Gateway will automatically scale to manage the increased load.
Security: API Gateway provides built-in authentication and authorization features to secure your API endpoints. You can implement API keys, AWS IAM roles, or other methods to control access to your backend resources.
Performance: API Gateway includes caching capabilities to improve response times and reduce backend load, enhancing performance. For example, frequently accessed endpoints can be cached to serve responses quickly without repeatedly invoking the backend services.
Monitoring and Analytics: API Gateway integrates with Amazon CloudWatch, providing detailed metrics and logging. This allows you to monitor API usage, track error rates, and troubleshoot issues, giving you insights into the number of form submissions and other vital statistics.
Cost-Effectiveness: With API Gateway, you only pay for the API calls you receive and the data transferred, making it a cost-effective option for applications with varying usage patterns.
- Seamless Integration with AWS Lambda:
- Direct Routing: API Gateway can directly route HTTP requests to your Lambda function, eliminating the need for intermediate servers.
- Automatic Scaling: As API Gateway scales with traffic, it automatically triggers more concurrent executions of your Lambda function.
- Simplified Development: You can set up API Gateway with Lambda integration quickly using the AWS Console or AWS SAM, reducing development time and complexity.
- End-to-End Serverless Architecture: This integration enables a complete serverless solution, including API endpoints, backend processing and AI content generation.
- API Versioning: API Gateway supports multiple API versions, allowing you to make updates without disrupting existing users.
Now that you understand the key benefits of using API Gateway, let’s get hands-on, where you will create and configure an API.
Yes, there are some sections that can be combined to streamline the content while maintaining clarity and flow. Here’s a revised structure where some steps have been grouped together:
Hands-On With API Gateway
To configure Amazon API Gateway for your serverless contact form solution, follow these tasks:
- Create and Configure a New REST API
- Set Up Resources and Methods
- Integrate the API with Your Lambda Function
- Test and Deploy the API
Task 1: Create and Configure a New REST API
- Access the API Gateway Service
- Go to the API Gateway service in the AWS Management Console.
- Click Create API and select REST API. Name the API ContactFormAPI.
- Choose the Appropriate Endpoint Type
- You will see three endpoint types: Regional, Edge-optimized, and Private.
- Choose Edge-optimized to route requests through Amazon CloudFront’s global points of presence, ensuring low latency for users worldwide.
- Regional deploys the API in the current AWS Region, suitable for local services.
- Private restricts API access to specified VPCs for internal applications.
- Edge-optimized routes requests through CloudFront’s global network, reducing latency for globally distributed users, ideal for your contact form.
Task 2: Set Up Resources and Methods
- Create a Resource for Handling Form Submissions
- Create a
/contactresource at the root level of your API, which will serve as the endpoint for form submissions. - Enable CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) to allow your static website to communicate with the API. This automatically adds an OPTIONS method to your resource to handle preflight requests from browsers.
- Create a
- Create a POST Method to Receive Form Data
- To handle form submissions, create a POST method for the
/contactresource:- Select the
/contactresource. - Click Create Method and choose POST.
- Select the
- To handle form submissions, create a POST method for the
Task 3: Integrate the API with Your Lambda Function
- Integrate with Lambda Function
- Configure the POST method to connect with your Lambda function to ensure that API Gateway can directly invoke the function whenever a client sends a request:
- Set the Integration type to Lambda Function.
- Enable Lambda Proxy Integration.
- Choose the AWS Region where your Lambda function is deployed.
- Enter the Lambda function name.
- Configure the POST method to connect with your Lambda function to ensure that API Gateway can directly invoke the function whenever a client sends a request:
- Configure Timeout
- Keep the default timeout of 29 seconds to ensure that the API Gateway connection terminates if the request processing exceeds this duration.
- Understand the Request Flow
- Review the request flow to understand how the API handles a request:
flowchart TD
A[Client] -->|Form Submission| B[Method Request: API Gateway receives the form data]
B -->|Receive Form Data| C[Integration Request: API Gateway prepares the data for Lambda]
C -->|Prepare Data| D[Lambda Integration: Lambda processes the data, generates AI quote, and prepares emails]
D -->|Process Data, Generate AI Quote, Prepare Emails| E[Integration Response: Adjust responses from Lambda]
E -->|Adjust Responses| F[Method Response: API Gateway packages the final response]
F -->|Package Final Response| G[Client: User receives confirmation email with AI-generated quote]
Task 4: Test and Deploy the API
Testing the API ensures that it receives form data correctly and that the Lambda function processes it as expected.
- Test the API Using API Gateway’s Built-In Tools
- Go to the POST method page and click the Test button.
- Enter the JSON object representing a form submission in the Request Body:
1 2 3 4 5
{ "name": "Test User", "email": "test@example.com", "message": "This is a test message." }
- Verify Results
- Click Test to send the test request to your Lambda function. Verify that the API receives the form data correctly and that the Lambda function processes it as expected. You should see a successful response and receive a confirmation email with the AI-generated quote.
- Deploy the API
- Click Deploy API and create a new deployment stage named prod (production).
- After deployment, API Gateway provides an Invoke URL. This URL is the endpoint you will integrate into your static website’s code for form submissions.
Your API is now deployed and ready for use, concluding the setup of your serverless contact form API in API Gateway.
Next, you will integrate your API with your static website, bringing all the components of your contact form system together to complete your serverless solution.
6. Frontend Integration
To complete the solution, integrate the contact form on the HTML5UP Dimensions static site template with your serverless backend by following these tasks:
- Customize the contact form in the HTML5 UP Dimensions template.
- Add JavaScript code for form submissions to enable API interaction.
- Connect the form to the serverless backend via the API Gateway.
- Test the solution.
flowchart TD
A[Visitor] -->|Submits Form| B[Contact Form on Static Website]
B -->|JavaScript Captures Data| C[API Gateway Endpoint]
C -->|Routes Request| D[Lambda Function]
D -->|Invokes Bedrock| E[Bedrock AI Integration]
E -->|Generates AI Quote| D
D -->|Sends Data to| F[Amazon SES]
F -->|Sends Emails| G[Visitor and Website Owner]
G -->|Receives Confirmation| H[Visitor's Inbox]
F -->|Receives Notification| I[Website Owner's Inbox]
Task 1: Customize the Contact Form
- Download and Prepare the Template
- Download the HTML5 UP Dimensions template files from the HTML5 UP website.
- Open the downloaded files in Visual Studio Code and install the Live Server extension to enable local testing.
- Modify the HTML Form
- Open the index.html file in VS Code and locate the contact section
<article id="contact"> - Replace the entire
<article id="contact">element with the following updated code:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30
<!-- Contact --> <article id="contact"> <h2 class="major">Contact</h2> <form method="post" action="#"> <div class="fields"> <div class="field half"> <label for="name">Name</label> <input type="text" name="name" id="name" required /> </div> <div class="field half"> <label for="email">Email</label> <input type="email" name="email" id="email" required /> </div> <div class="field"> <label for="message">Message</label> <textarea name="message" id="message" rows="4" required></textarea> </div> </div> <ul class="actions"> <li><input type="submit" value="Send Message" class="primary" /></li> <li><input type="reset" value="Reset" /></li> </ul> </form> <ul class="icons"> <li><a href="#" class="icon brands fa-twitter"><span class="label">Twitter</span></a></li> <li><a href="#" class="icon brands fa-facebook-f"><span class="label">Facebook</span></a></li> <li><a href="#" class="icon brands fa-instagram"><span class="label">Instagram</span></a></li> <li><a href="#" class="icon brands fa-github"><span class="label">GitHub</span></a></li> </ul> </article>
- Open the index.html file in VS Code and locate the contact section
This updated code incorporates the required attributes for all input fields to leverage HTML5 form validation, sets the email input type to email for email validation, and uses a textarea for the message input to allow longer messages.
Task 2: Add JavaScript for Form Submission
To enable the contact form on your static website to interact with the serverless backend, you need to add JavaScript, which captures form submissions, sends the data to your API Gateway endpoint, and provides feedback to the user based on the server’s response.
- Open the
main.jsFile- In Visual Studio Code, go to the assets > javascript directory and open the main.js file.
- Add the JavaScript Code for Form Handling
- Scroll to the end of the main.js file, and just before the
})(jQuery);line, copy the following code and paste it there:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37
// Contact form handling var $contact = $('#contact'); var $form = $contact.find('form'); var $submit = $form.find('input[type="submit"]'); $form.submit(function(event) { event.preventDefault(); // Disable submit button (using template's existing disabled class) $submit.addClass('disabled'); // Send data asynchronously $.ajax({ url: "YOUR_API_ENDPOINT_HERE", type: "POST", data: JSON.stringify(Object.fromEntries(new FormData($form[0]))), contentType: "application/json", success: function(result) { $form.find('.response').remove(); $form.append('<div class="response success">Message sent successfully!</div>'); $form[0].reset(); // Close the form after 3 seconds using template's hash navigation setTimeout(function() { location.hash = ''; }, 3000); }, error: function(error) { $form.find('.response').remove(); $form.append('<div class="response error">There was an error sending your message. Please try again.</div>'); }, complete: function() { // Re-enable submit button $submit.removeClass('disabled'); } }); });
- Scroll to the end of the main.js file, and just before the
- Save Your Changes
Key Functions of the JavaScript Code
- Captures form submissions by listening for events and preventing default browser behavior
- Sends form data to your API asynchronously using AJAX
- Provides real-time user feedback with success or error messages
- Manages form state by disabling the submit button during submission
- Integrates with template navigation for seamless user experience
Task 3: Connect the Form to the Serverless Backend via API Gateway
To connect the contact form on your static website to your serverless backend, you need to ensure that the form data is correctly sent to the API Gateway endpoint you’ve created.
- Replace the API Endpoint
In the
main.jsfile, replace the placeholder'YOUR_API_ENDPOINT_HERE'with the actual API Gateway Invoke URL for your contact form endpoint.- To find the full invoke URL for your endpoint, go to the Stages section in the API Gateway console, select the prod stage, go to the ‘contact’ resource, and click on the POST method.
- Copy the full URL and paste it in the JavaScript code where the API endpoint is specified.
Task 4: Test the Solution
Now that you’ve integrated your contact form with the serverless backend, test its functionality using the Live Server extension in Visual Studio Code.
- Save All Changes and Test Locally
- Open your HTML file with the Live Server extension to view it in your web browser.
- Fill out the contact form with your own name, email address, and a test message. Click Send Message to submit the form.
- Observe the Form Behavior
- Notice how the submit button becomes disabled after submission, preventing multiple submissions. After a moment, a success message should appear, indicating that the form has been submitted successfully.
- Check Your Email Inbox
- Check your email inbox for two emails:
- One containing the test message you sent.
- Another with a confirmation email that includes the AI-generated inspirational quote.
- Check your email inbox for two emails:
- Test Error Handling
- Try submitting the form with invalid data, such as an incorrect email format, or submit an empty form to confirm that the HTML5 validation works properly.
- For a more thorough test, temporarily change the API endpoint to an invalid URL in the JavaScript file. This will help verify that error messages display correctly when the form submission fails. Remember to revert the URL back to the correct API endpoint after testing.
This testing ensures that your contact form is fully functional, accurately handling valid and invalid inputs, and operating as expected