Building a Bedrock Agent With AWS News Search
Build an Amazon Bedrock agent that queries the AWS News Blog RSS feed and answers questions about recent AWS announcements. Use Lambda action groups to fetch and parse the feed, expose the agent through Amazon API Gateway, and provide a terminal-style web UI.
Overview
The agent → awsnews.digitalden.cloud
This post explains how to build an Amazon Bedrock agent that searches the AWS News Blog RSS feed to answer questions about recent AWS announcements. When you ask questions such as “What’s new with AWS Lambda?” or “Are there any recent Amazon Bedrock updates?”, the agent retrieves the live RSS feed, identifies relevant posts, and returns summaries with direct links to the original articles.
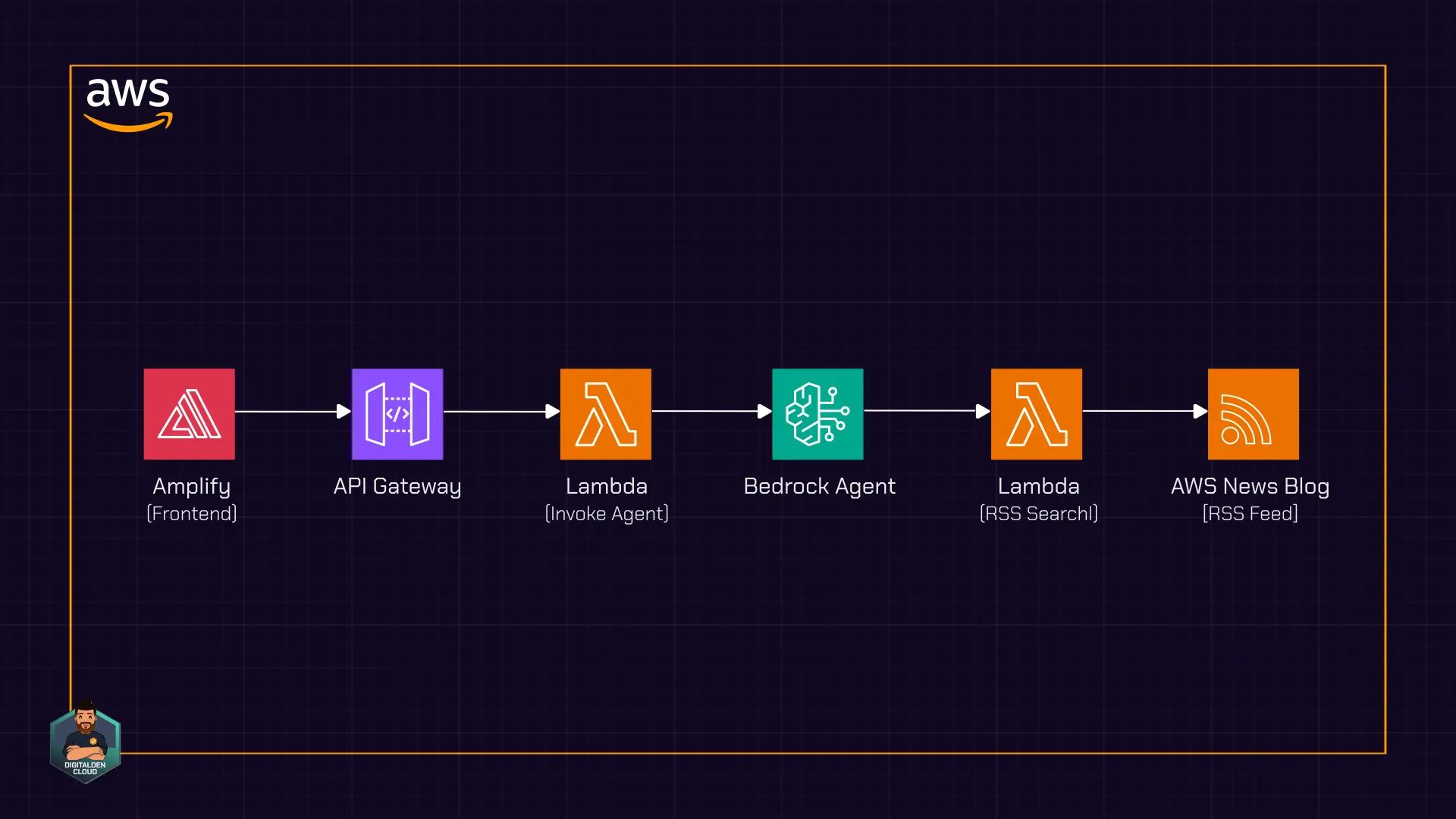
The frontend is a terminal-style web interface hosted using AWS Amplify. The UI sends requests to Amazon API Gateway, which invokes a Lambda function responsible for calling the Bedrock agent. When the agent needs current information, it invokes a second Lambda function through an action group. That function fetches and parses the RSS feed in real time.
The architecture does not use a database or a Bedrock knowledge base. The agent relies entirely on on-demand RSS retrieval and parsing performed by a Lambda function, keeping the implementation minimal and focused on live content access.
Watch the video:
Demo
Problem
A foundation model can answer general AWS questions from its training data. Ask “What is Lambda?” and it provides a solid explanation. However, if you ask “What’s new with Lambda?”, the model cannot answer reliably. The model’s knowledge has a cutoff date. It does not know what AWS announced last week, what features launched yesterday, or what is currently in preview.
Worse, the model may not acknowledge this gap. Ask about a newer service like AWS DevOps Agent and the model might generate a confident, detailed explanation of features that sound plausible but are entirely fabricated. This is hallucination. The model produces information based on patterns rather than facts, and without access to live data, there is no way to verify accuracy.
Solution
Build a Bedrock agent and give it a tool that searches live data. That tool is a Lambda function that searches the AWS News Blog RSS feed.
When you ask “Any recent Bedrock updates?”, the agent recognises it needs current information. It invokes an action group, which triggers the Lambda function. The function fetches the live RSS feed, searches for matching posts, and returns them to the agent. The agent then responds with actual recent announcements, complete with titles, descriptions, and links.
Architecture
A user enters a question in a terminal-style UI hosted using AWS Amplify. The browser sends a POST request to Amazon API Gateway, which invokes an AWS Lambda function. That function calls the Amazon Bedrock agent with the user’s prompt.
The agent evaluates the request and determines how to respond. If the question requires current AWS announcements, the agent invokes an action group. The action group triggers a second Lambda function that retrieves and searches the AWS News Blog RSS feed.
flowchart LR
UI[Amplify Terminal UI]
--> APIGW[API Gateway]
--> L1[Invoker Lambda]
--> BA[Bedrock Agent]
BA -->|AWS News query| AG[Action Group]
AG --> L2[RSS Search Lambda]
L2 --> BA
BA -->|No tool required| FM[Foundation Model]
An action group defines the tools available to the agent. It establishes a contract between the agent and the Lambda function using an OpenAPI schema that specifies the operation and input parameters. When the agent determines that RSS search is required, it invokes the action group and passes the query parameters defined in the schema.
The agent controls orchestration. It decides whether to answer directly using its model context or invoke a tool to retrieve external data. This decision logic distinguishes an agent from a direct model invocation.
Step 1: RSS Lambda
The agent requires a tool that can retrieve current data. In this step, you complete the following tasks:
- Create a Lambda function that fetches the AWS News Blog RSS feed
- Add code that parses the feed and searches for relevant posts
- Configure permissions so the Bedrock agent can invoke the function
Open the Lambda console and create a new function:
- Function name:
search-aws-news - Runtime: Python 3.12
- Architecture: x86_64
- Permissions: Create a new role with basic Lambda permissions
Basic Lambda permissions create an IAM role that allows the function to write logs to CloudWatch. The agent requires additional permissions to invoke this function, which you configure later in this step.
Create the function.
In the code editor, replace the existing code with the following:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
import json
import urllib.request
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Get the search topic from the agent
topic = ""
for param in event.get("parameters", []):
if param.get("name") == "topic":
topic = param.get("value", "").lower()
if not topic:
return build_response(event, [])
# Fetch the AWS News Blog RSS feed
feed_url = "https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/feed/"
with urllib.request.urlopen(feed_url, timeout=10) as response:
feed_data = response.read().decode("utf-8")
# Parse and search
root = ET.fromstring(feed_data)
matching_posts = []
topic_words = topic.split()
# Adjust these values to control results (increases token usage)
MAX_POSTS_TO_SEARCH = 20 # Number of recent posts to evaluate
MAX_RESULTS = 5 # Maximum matching results to return
DESC_LENGTH = 150 # Characters to include from description
for item in root.findall(".//item")[:MAX_POSTS_TO_SEARCH]:
title = item.find("title").text
link = item.find("link").text
description = item.find("description").text or ""
if all(word in title.lower() or word in description.lower() for word in topic_words):
matching_posts.append({
"title": title,
"link": link,
"description": description[:DESC_LENGTH] + "..."
})
if len(matching_posts) >= MAX_RESULTS:
break
return build_response(event, matching_posts)
def build_response(event, posts):
return {
"messageVersion": "1.0",
"response": {
"actionGroup": event.get("actionGroup", ""),
"apiPath": event.get("apiPath", ""),
"httpMethod": event.get("httpMethod", ""),
"httpStatusCode": 200,
"responseBody": {
"application/json": {
"body": json.dumps(posts) if posts else json.dumps({"message": "No matching posts found."})
}
}
}
}
Deploy the function.
The function uses Python’s built-in
urllibandxmllibraries to retrieve and parse the RSS feed. There is no dependency packaging step, which keeps the deployment simple and the Lambda function small.
The AWS News Blog RSS feed can contain a large amount of text across multiple entries. Passing the full feed to the agent would increase token usage and slow down responses. The function applies three limits to control payload size:
- Only the most recent 20 posts are evaluated, restricting the search to recent announcements
- Post descriptions are truncated to 150 characters, providing context without including the full article text
- A maximum of 5 matching results is returned, ensuring the response remains concise and readable
These values work well for a demo, but you can adjust them in the code. Increasing the post count or max results will improve coverage at the cost of higher token usage and slower responses.
Lambda permissions
Grant Amazon Bedrock permission to invoke the function. In the Lambda console, open the Configuration tab and select Permissions. Under Resource-based policy statements, choose Add permissions.
Configure the statement as follows:
- Statement ID:
AllowBedrockInvocation - Principal:
bedrock.amazonaws.com - Source ARN:
arn:aws:bedrock:us-east-1:123456789012:agent/* - Action:
lambda:InvokeFunction
Replace the Region and account ID with your own values. The wildcard allows any Bedrock agent in the account to invoke the function. To restrict invocation to a single agent, replace the wildcard with the agent ID after the agent is created.
Save the permissions.
Step 2: Bedrock Agent
With the RSS Lambda function deployed, create the Bedrock agent that uses it. In this step, you complete the following tasks:
- Configure the agent and select a foundation model
- Define the system prompt that controls agent behaviour
- Connect the agent to the Lambda function through an action group
- Configure IAM permissions so the agent can invoke the function
Open the Amazon Bedrock console, select Agents from the navigation pane, and create a new agent:
- Agent name:
aws-news-agent
The Agent builder opens.
Under Agent resource role, leave Create and use a new service role selected. This role grants the agent permission to invoke the foundation model and call configured action groups. Bedrock creates and manages this role automatically.
Under Model, select a foundation model. The model interprets user requests and determines when to invoke tools. Smaller models have lower cost and faster response times. Larger models provide stronger reasoning capabilities and improved tool selection accuracy.
Foundation models have a fixed knowledge cutoff date. They do not have awareness of AWS announcements or features released after training. This is why the agent is configured with a tool that retrieves current data from the AWS News Blog.
In the Instructions for the Agent field, enter the following system prompt:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
You are a helpful assistant that answers questions about AWS news and announcements.
RULES:
- For any question about recent, current, or new AWS announcements, features, or updates, use the SearchAWSNews function. Do not answer from your training data.
- Never guess what news exists. Always search first.
- If a search returns no results for a specific service, try a broader search term automatically or report no results found.
- If no results are found after searching, say so clearly and offer to help with general AWS questions instead.
- For general AWS questions not about recent news, answer directly from your knowledge.
FORMATTING:
- Use plain text only. No markdown syntax of any kind.
- Do not use asterisks, bold, italics, headers, bullet points, or special characters for emphasis.
- Present search results as a numbered list.
- For each result, show the title, a one-sentence description, and the link on separate lines.
- Display links exactly as returned by the search. Do not modify URLs.
- Apply these formatting rules to every response, including follow-up searches.
Example output format:
1. AWS Lambda Durable Functions
New capability for building multi-step applications and AI workflows.
Link: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/example-post/
2. Database Savings Plans
New pricing model for AWS databases offering cost efficiency with flexibility.
Link: https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/another-example/
Be concise, friendly, and helpful.
The system prompt removes ambiguity. Without clear rules, the agent might try to answer news questions from its training data instead of searching. The explicit instruction to use the SearchAWSNews function first ensures it calls the tool when needed.
Save the agent.
Action group
An action group connects the agent to external tools such as Lambda functions. It defines the operation, input parameters, and response format so the agent can invoke the tool correctly.
In the Action groups section, add a new action group:
- Action group name:
SearchAWSNews - Action group type: Define with function details
Under Action group function, choose Select an existing Lambda function and select the search-aws-news function.
For Action group schema, select Define via in-line schema editor and replace the existing schema with the following:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
openapi: 3.0.0
info:
title: AWS News Search API
version: 1.0.0
description: API to search the AWS News Blog RSS feed.
paths:
/search-news:
get:
summary: Searches the AWS News Blog for posts matching a topic.
description: Fetches the RSS feed and returns matching posts with titles, descriptions, and links.
operationId: searchNews
parameters:
- name: topic
in: query
description: The topic to search for, such as Lambda, Bedrock, or S3
required: true
schema:
type: string
responses:
'200':
description: A list of matching posts.
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
posts:
type: array
items:
type: object
properties:
title:
type: string
link:
type: string
description:
type: string
This schema tells Bedrock what the tool does, what input it expects, and what response to return. The operationId becomes the function name the agent sees.
Create the action group and save the agent.
Select Prepare to compile the agent configuration.
Agent permissions
The agent’s IAM role requires permission to invoke the Lambda function. Open the agent details page and locate the service role under Permissions. Select the role to open it in the IAM console.
On the Permissions tab, create an inline policy. Switch to JSON view and paste the following:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "lambda:InvokeFunction",
"Resource": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:123456789012:function:search-aws-news"
}
]
}
Replace the Region and account ID with your own values.
Name the policy BedrockAgentLambdaInvoke and create it.
Return to the Bedrock console and prepare the agent again.
Step 3: Test the Agent
With the agent configured, test it in the Amazon Bedrock console and review the trace to understand how the agent reasons and invokes tools.
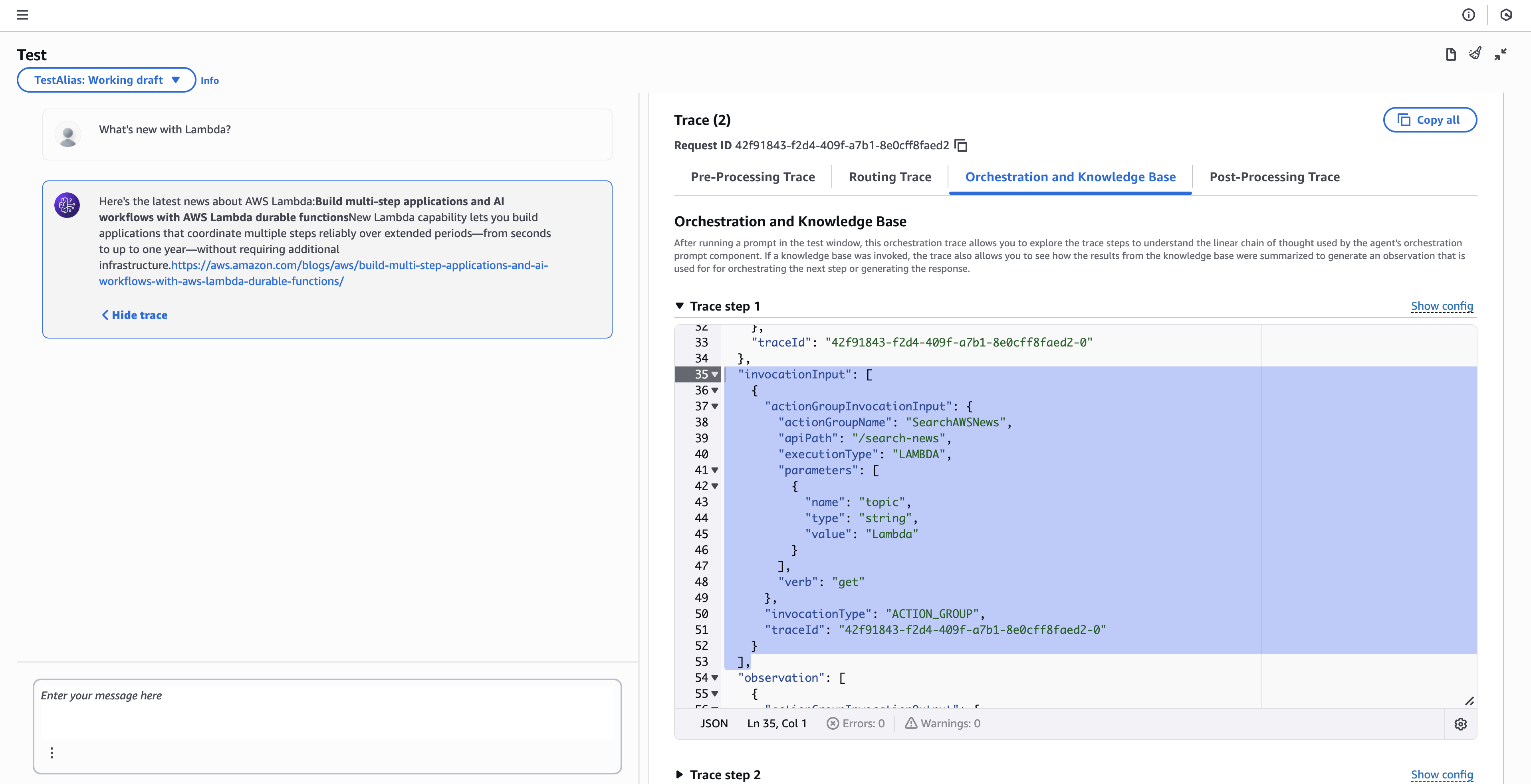
Open the agent details page. In the Test panel, confirm that the alias dropdown is set to TestAlias: Working draft.
In the chat input, enter What's new with Lambda?.
The agent processes the request, invokes the RSS Lambda function through the action group, and returns matching posts from the AWS News Blog.
The exact response varies based on recent AWS announcements.
Reading the trace
The trace confirms that the agent invoked the expected action group. In the trace output, the agent selects the SearchAWSNews action group and executes it through Lambda. The topic parameter is passed with the value Lambda, which matches the user query.
This confirms that the agent identified the request as requiring current information and delegated the search to the Lambda function instead of answering from model training data.
Step 4: Invoker Lambda
The Bedrock agent is currently accessible only from the console. In this step, you create a Lambda function that acts as an integration layer between the frontend and the agent. This function receives requests from API Gateway, invokes the agent, and returns the response.
flowchart LR
F[Frontend]
--> AG[API Gateway]
--> L[Invoker Lambda]
--> B[Bedrock Agent]
In this step, you complete the following tasks:
- Create a Lambda function that invokes the Bedrock agent
- Configure the function to handle requests from API Gateway
- Grant permissions so the function can invoke the agent
Open the Lambda console and create a new function:
- Function name:
invoke-agent - Runtime: Python 3.12
- Architecture: x86_64
- Permissions: Create a new role with basic Lambda permissions
Create the function.
In the code editor, replace the existing code with the following:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
import json
import boto3
def lambda_handler(event, context):
# Parse the request body
try:
if 'body' in event:
body = event.get('body', '{}')
if isinstance(body, str):
body = json.loads(body)
else:
body = event
message = body.get('message', '')
session_id = body.get('sessionId', 'default-session')
except Exception as e:
return {
'statusCode': 400,
'headers': cors_headers(),
'body': json.dumps({'error': f'Invalid request body: {str(e)}'})
}
if not message:
return {
'statusCode': 400,
'headers': cors_headers(),
'body': json.dumps({'error': 'No message provided'})
}
# Bedrock agent identifiers
AGENT_ID = 'YOUR_AGENT_ID'
AGENT_ALIAS_ID = 'TSTALIASID'
try:
client = boto3.client('bedrock-agent-runtime')
response = client.invoke_agent(
agentId=AGENT_ID,
agentAliasId=AGENT_ALIAS_ID,
sessionId=session_id,
inputText=message
)
completion = ""
for event in response.get('completion', []):
if 'chunk' in event:
completion += event['chunk']['bytes'].decode('utf-8')
return {
'statusCode': 200,
'headers': cors_headers(),
'body': json.dumps({'response': completion})
}
except Exception:
return {
'statusCode': 500,
'headers': cors_headers(),
'body': json.dumps({'error': 'Failed to get response from agent'})
}
def cors_headers():
return {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Access-Control-Allow-Origin': '*',
'Access-Control-Allow-Headers': 'Content-Type',
'Access-Control-Allow-Methods': 'POST, OPTIONS'
}
Replace YOUR_AGENT_ID with the agent ID from the Bedrock console.
This example uses
TSTALIASID, the default test alias. For production deployments, create a versioned alias that points to a specific agent version.
The sessionId parameter maintains conversation context across multiple requests. When the same session ID is passed with subsequent messages, the agent retains memory of previous exchanges, enabling follow-up questions like “Tell me more about the first one” without repeating context. The frontend generates a unique session ID per browser session and includes it with each request.
Deploy the function.
Function configuration
Open Configuration and select General configuration. Increase Timeout to 30 seconds and save the changes.
Permissions
Open Configuration and select Permissions. Select the execution role to open it in the IAM console.
Add an inline policy. Switch to JSON view and paste the following:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": "bedrock:InvokeAgent",
"Resource": "arn:aws:bedrock:us-east-1:123456789012:agent-alias/*/*"
}
]
}
Replace the Region and account ID with your own values.
Name the policy BedrockInvokeAgent and create it.
Step 5: API Gateway
The invoker Lambda function requires an HTTP endpoint so the frontend can send requests. In this step, you create a REST API in Amazon API Gateway, connect it to the Lambda function, enable CORS, and deploy the API.
In this step, you complete the following tasks:
- Create a REST API in API Gateway
- Add a POST method that invokes the Lambda function
- Enable CORS for browser-based requests
- Deploy the API and obtain the invoke URL
Open the API Gateway console and create a new API:
- API type: REST API
- API name:
aws-news-agent-api
Create the API.
Create a resource and method
In the Resources panel, select Create resource:
- Resource name:
agent - CORS: Enabled
Create the resource.
With the /agent resource selected, select Create method:
- Method type: POST
- Integration type: Lambda Function
- Lambda proxy integration: Enabled
- Lambda function:
invoke-agent
Create the method.
Lambda proxy integration forwards the full HTTP request to the Lambda function without modification. The function receives the request body and headers and must return a response that includes a status code and headers.
Deploy the API
Select Deploy API:
- Stage: New stage
- Stage name:
prod
Deploy the API.
After deployment, note the Invoke URL. The full endpoint used by the frontend is the invoke URL with the /agent resource appended:
1
https://abc123xyz.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/prod/agent
Test the endpoint
Before building the frontend, validate the API using AWS CloudShell or your terminal. Set your endpoint as a variable:
1
ENDPOINT="https://abc123xyz.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/prod/agent"
Then send a request to the API Gateway endpoint:
1
2
3
curl -X POST $ENDPOINT \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"message": "What is new with Lambda?", "sessionId": "test-123"}'
A JSON response with the agent’s answer confirms that API Gateway, the Lambda function, and the Bedrock agent are connected correctly.
Step 6: Amplify
The final step is to deploy the frontend. In this step, you download the terminal-style UI, update it with your API Gateway endpoint, and deploy it using AWS Amplify.
In this step, you complete the following tasks:
- Download the frontend from GitHub
- Update the API endpoint configuration
- Deploy the frontend using AWS Amplify
Download the frontend
Open the following GitHub repository:
1
https://github.com/digitaldencloud/aws-news-agent-frontend
Select the index.html file, select Raw, then right-click and save the file locally.
Update the API endpoint
Open index.html in a text editor and locate the following line:
1
const API_ENDPOINT = 'YOUR_API_GATEWAY_URL';
Replace it with your API Gateway endpoint:
1
const API_ENDPOINT = 'https://abc123xyz.execute-api.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/prod/agent';
Save the file.
Deploy to AWS Amplify
Create a ZIP archive containing index.html.
Open the AWS Amplify console and select Create new app:
- Deployment method: Deploy without Git
- App name:
aws-news-agent - Branch name:
main - Method: Drag and drop
Upload the ZIP file and select Save and deploy.
After deployment completes, Amplify provides a public URL:
1
https://main.d1abc123.amplifyapp.com
Open the URL in a browser. The terminal-style UI loads and sends requests to the API Gateway endpoint.
Enter a query, for example What's new with Lambda?, to verify end-to-end communication between the frontend, API Gateway, Lambda, and the Bedrock agent.
AWS Amplify provides HTTPS by default, so the frontend is served securely without additional configuration.
To use a custom domain, go to Hosting > Custom domains in the Amplify console. Enter your subdomain (e.g.
awsnews.yourdomain.com) and follow the steps to configure DNS. Amplify handles SSL certificate provisioning automatically.
Summary
This post demonstrated how to build an Amazon Bedrock agent that answers questions about recent AWS announcements by searching the AWS News Blog RSS feed in real time. The agent uses an action group to invoke a Lambda function when current information is required, rather than relying on model training data.
You exposed the agent through an invoker Lambda function and a REST API in Amazon API Gateway, then deployed a terminal-style frontend using AWS Amplify. The frontend sends user queries to the API, which routes requests through Lambda to the Bedrock agent and returns responses to the browser.
Without access to live data, foundation models may hallucinate when asked about newer services or recent announcements. Connecting the agent to an external data source addresses this limitation by grounding responses in verified, up-to-date information.
This implementation shows how Bedrock agents can be extended with external data sources using Lambda action groups, allowing foundation model reasoning to be combined with live data access in a lightweight, serverless architecture.