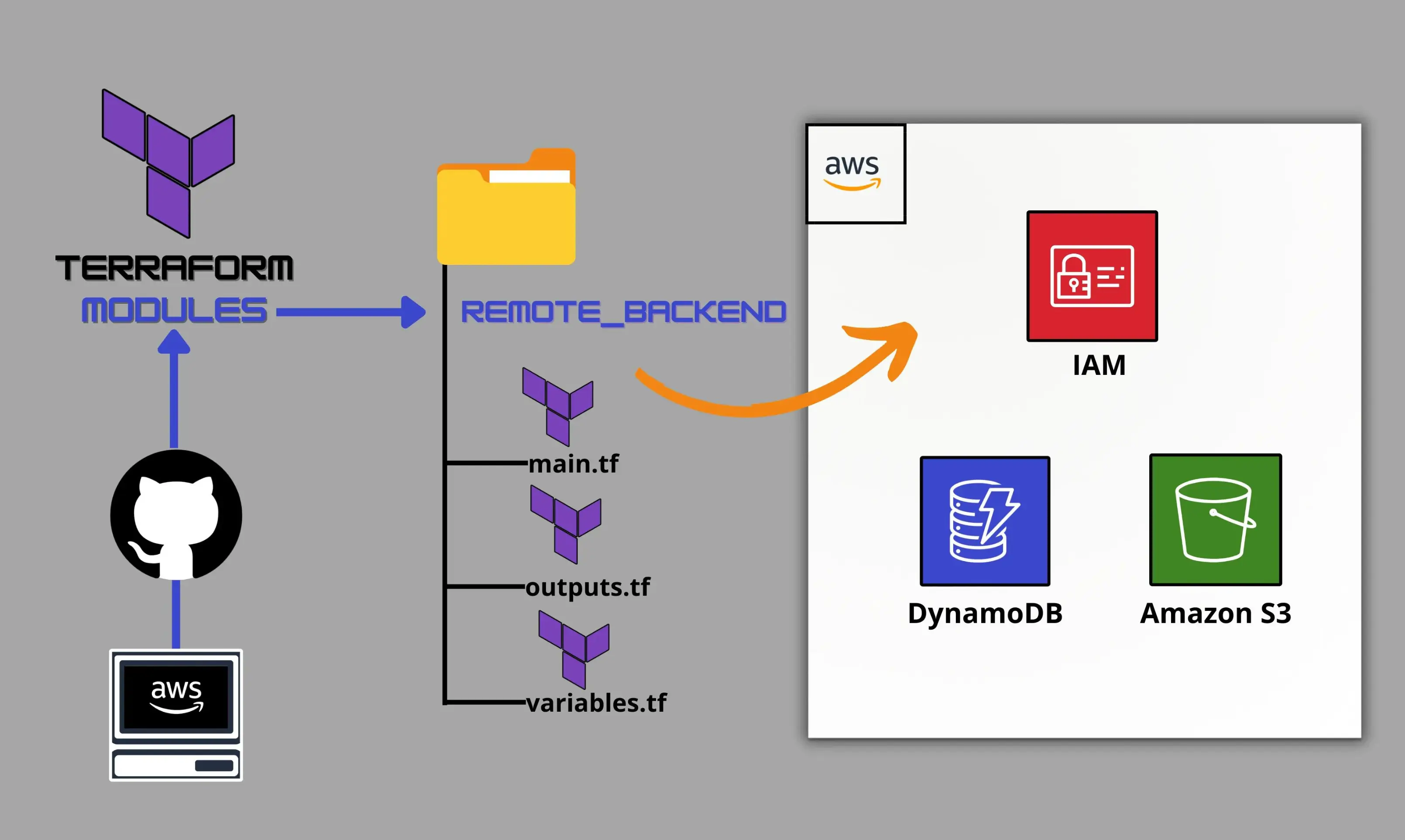
Creating a Terraform Module for S3 Remote Backend with DynamoDB State Locking
Create a Terraform module that provisions an S3 bucket to store the terraform.tfstate file and a DynamoDB table to lock the state file to prevent concurrent modifications and state corruption.
Setting up Terraform state management on AWS can be tricky. The process involves configuring a remote backend, which can be complex. If you’re new to Terraform and using an S3 bucket and DynamoDB for state management, you’ll face a challenge. You need to set up your resources with Terraform, but configuring the Terraform backend with Terraform is difficult, and is often referred to as the chicken and egg problem.
In a previous post, Setting Up Terraform Remote Backend With AWS Using A Bash Script I showed a solution using a Bash script to deploy AWS backend resources. This made starting your Terraform infrastructure faster and efficient. The Bash script creates the Terraform backend resources, then Terraform uses these resources for its backend. This ensures Terraform knows and manages its state with AWS resources effectively. Today, I’ll share another solution:
Creating a Reusable Terraform Module that Provisions the S3 Remote Backend
Benefits of Using a Reusable Terraform Module
- Consistency Across Projects: A module for an S3 remote backend ensures that the backend is configured consistently across different projects.
- Reusability: Once you create a module for an S3 backend, it can be reused in multiple Terraform projects. This saves time as you don’t need to write or copy the same configuration code for each new project that requires an S3 backend.
- Simplicity: A module removes the complexity of setting up an S3 backend. Users of the module don’t need to understand all the details of S3 and Terraform backend configurations; they can simply use the module with a few inputs to get the backend up and running.
- Efficient Collaboration: When working in a team, a module for the S3 backend helps ensure that everyone is using the same configuration, making collaboration easier and more efficient.
Objectives
- Creating a remote backend module with variables and outputs.
- Integrating the backend module in your root module’s main.tf.
- Initializing Terraform and deploying backend resources.
- Configuring and transitioning to an S3 remote backend.